
Age can also affect absorption of dietary calcium. Absorption of calcium from food is about 45% at intakes of 200 mg/day but only 15% when intakes are higher than 2,000 mg/day. Īn inverse relationship exists between calcium intake and absorption. These levels remain constant in men, but they start to drop in women as a result of increases in bone remodeling due to decreased estrogen production at the start of menopause. This amount rises quickly after birth, reaching about 1,200 g in women and 1,400 g in men by adulthood. Īt birth, the body contains about 26 to 30 g calcium. Bone remodeling is required to change bone size during growth, repair damage, maintain serum calcium levels, and provide a source of other minerals. Unlike teeth, bone undergoes continuous remodeling, with constant resorption and deposition of calcium into new bone. More than 99% of calcium in the body is in the form of calcium hydroxyapatite, an inorganic matrix of calcium and phosphate that is stored in the bones and teeth. Īlmost all (98%) calcium in the body is stored in the bones, and the body uses the bones as a reservoir for, and source of, calcium to maintain calcium homeostasis. Vitamin D is required for calcium to be absorbed in the gut by active transport and to maintain adequate calcium levels in blood. Active transport is responsible for most absorption when calcium intakes are lower, and passive diffusion accounts for an increasing proportion of calcium absorption as intakes rise. Ĭalcium from foods and dietary supplements is absorbed by both active transport and by passive diffusion across the intestinal mucosa. The small ionized pool of calcium in the circulatory system, extracellular fluid, and various tissues mediates blood vessel contraction and dilation, muscle function, blood clotting, nerve transmission, and hormonal secretion. IntroductionĬalcium, the most abundant mineral in the body, is found in some foods, added to others, present in some medicines (such as antacids), and available as a dietary supplement.Ĭalcium makes up much of the structure of bones and teeth and allows normal bodily movement by keeping tissue rigid, strong, and flexible. For a general overview of Calcium, see our consumer fact sheet on Calcium. is a fact sheet intended for health professionals.Introduction to the National Employment Standards fact sheet.Find an enterprise agreement – Fair Work Commission.Source reference: Fair Work Act 2009 s.61 See Casual employees for more information. they reasonably expect to continue being employed by the employer on a regular and systematic basis.they have been employed by their employer as a casual employee on a regular and systematic basis over at least 12 months, and.In some states and territories, long serving casuals are eligible for long service leave.Ĭasual employees can request flexible working arrangements and take unpaid parental leave if: the Fair Work Information Statement (the FWIS) and the Casual Employment Information Statement (the CEIS).paid or unpaid family and domestic violence.offers and requests to convert from casual to permanent employment.Casual employees and the NESĬasual employees only get some NES entitlements including: This is regardless of the award, registered agreement or employment contract that applies. Fair Work Information Statement (the FWIS) and Casual Employment Information Statement (the CEIS).Īll employees in the national workplace relations system are covered by the NES.Notice of termination and redundancy pay.Personal/carer's leave, compassionate leave and family and domestic violence leave.Parental leave and related entitlements.Offers and requests to convert from casual to permanent employment.Requests for flexible working arrangements.The 11 minimum entitlements of the NES are: enterprise agreement or other registered agreement.Įmployers have to give every new employee a copy of the Fair Work Information Statement (the FWIS) when they start their new job.Įmployers also have to give every new casual employee a copy of the Casual Employment Information Statement (the CEIS) at the same time.Other workplace instruments can't provide for conditions that are less than the National Minimum Wage or the NES. The National Minimum Wage and the NES make up the minimum entitlements for employees in Australia. The National Employment Standards (NES) are 11 minimum employment entitlements that have to be provided to all employees.
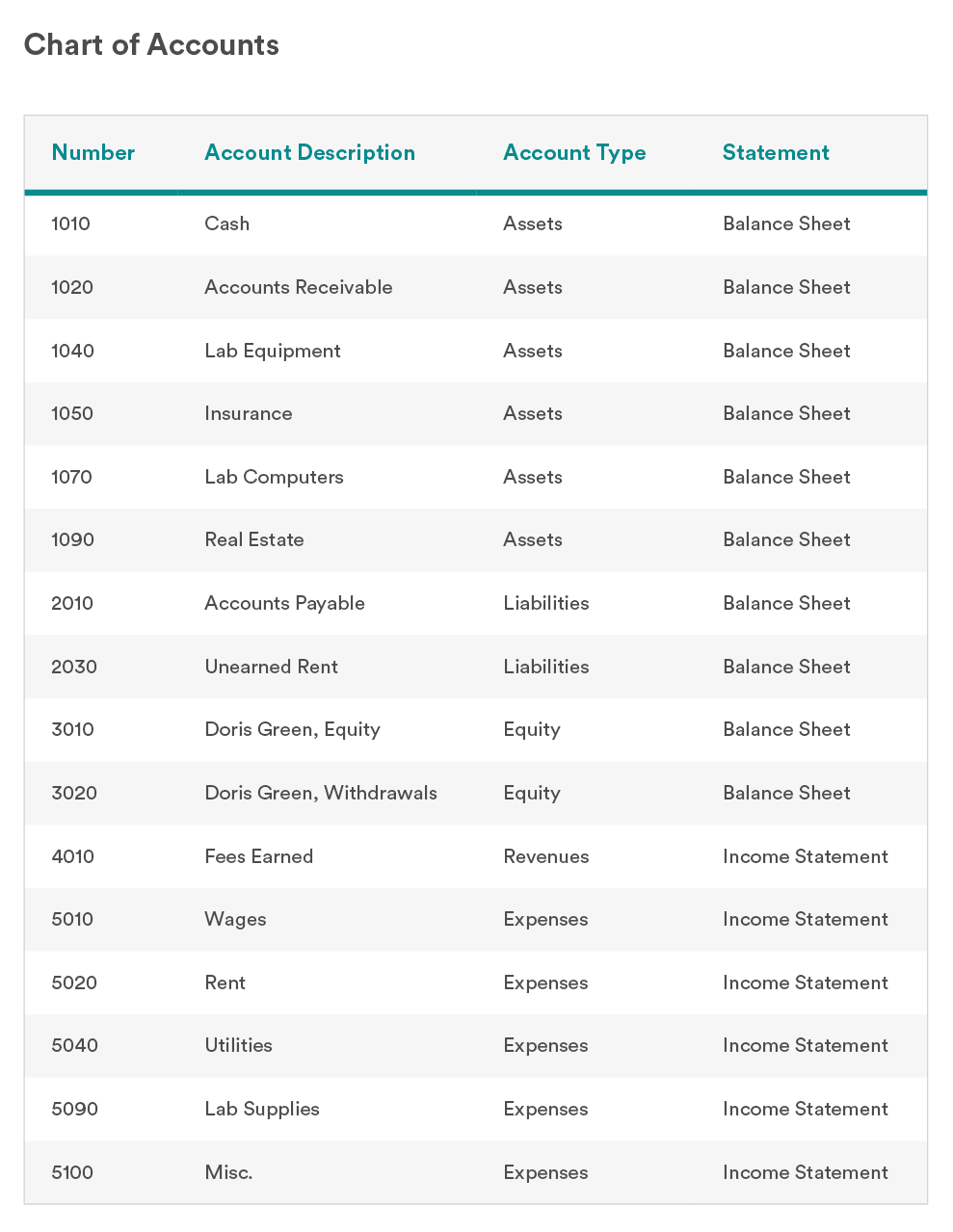
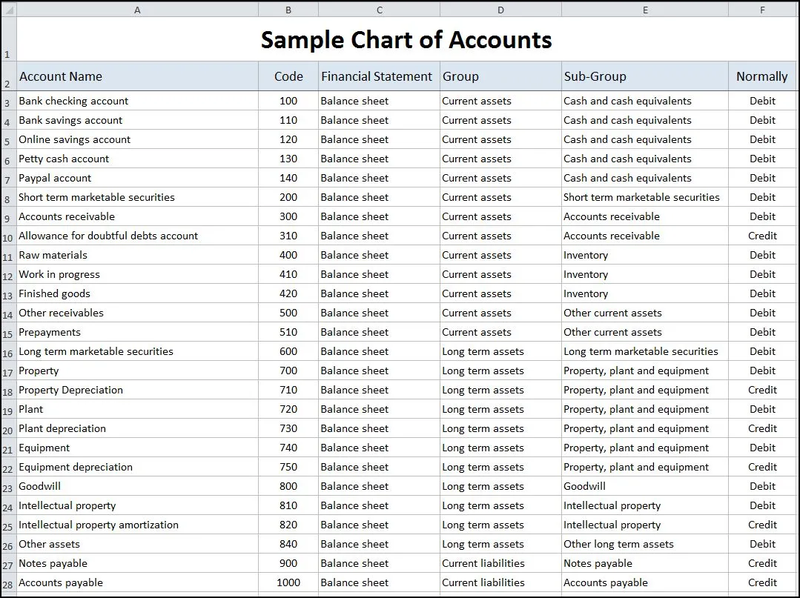
Bullying, sexual harassment & discrimination at work.Casual Employment Information Statement.Pay during inclement or severe weather & natural disasters.Allowances, penalty rates & other payments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
